Custom Paging in GridView Using LINQ
What is LINQ?
LINQ stands for Language Integrated Query. LINQ is a data querying methodology that provides querying capabilities to .Net languages which have similar syntax like SQL query. LINQ has a set of querying operators that can be used to query in memory object collection, Sql database, XML, etc. The LINQ processing engine will convert the LINQ query to native query specific to the database on execution. Since, querying feature is integrated with the language; one can build an efficient query with the language of their choice. To support LINQ development, Visual Studio provides intellisense support and with language support, we have type safety and compile-time error checks.
Moving forward, we will build custom paging for GridView control using LINQ to SQL classes.
What is LINQ to SQL classes?
LINQ to SQL is another capability which we can use to manage the relational database object as .net object. We can query, insert, update and delete the underlying database object with these classes. When we query/update/delete these .net object, LINQ to SQL will automatically take care of the underlying relational data objects operations. In short, LINQ to SQL provides an Object-Relational Mapping (O/R Mapping) which maps objects of different type system. In our case, it is relational to object oriented type system.
With these information’s, we will move to our subject matter with these introductions.
To understand the custom paging implementation, we will bind the GridView with employee data. The sample will contain 2 tables, Employee and Department in APP_Data folder. We will bind the GridView with the data fetched from the database using LINQ to SQL classes.
Note
There are lots of talks that LINQ to SQL is no more and it should not be preferred. The talks are that LINQ to entity should be preferred instead of LINQ to SQL. But, Microsoft still supports it and has plans to improve it further. Read more here.
Binding GridView and Providing Custom Paging
We will bind the GridView control using ObjectDataSource control and will use the inbuilt pager in GridView control to provide the paging. The ObjectDataSource control in turn will use LINQ to interact with database.
Steps
1. Open Visual Studio 2008.
2. Click New > Website > Select ASP.Net Website. I have selected C# as the language.
3. Drag a GridView control and ObjectDataSource control into our ASPX page.
Designing the LINQ to SQL classes
I assume you have already created a SqlExpress database in APP_Data folder with Employee and Department table.
Open Server Explorer, Expand the database tables.
Drag Employee and Department into LINQ to SQL designer. The LINQ to SQL Objects will be created automatically. Refer the below figure.
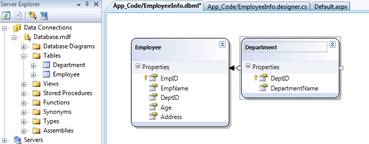
Thus, our LINQ to SQL class is ready. Next, we will configure our ObjectDataSource and GridView control to display the data with custom paging.
Configuring ObjectDataSource control and GridView control
In order to make ObjectDataSource control to work we need to set the following properties.
EnablePaging
This property accepts a Boolean to enable paging with ObjectDataSource control. Set it to true.
SelectCountMethod
We need to specify the name of the method that can fetch the total number of records available in the database.
SelectMethod
This property will accept the name of the method that fetches actual database record.
TypeName
This property needs to be configured with the class or type name that has the implementation of SelectCountMethod and SelectMethod.
StartRowIndexParameterName
This property will accept the start row index of the record to fetch from database.
MaximumRowsParameterName
This property will accept the maximum number of rows that can be fetched at one time. This will be equivalent to page size.
The data access class will use LINQ to fetch the data from the database. Refer the below code,
public class EmployeeDAO
{
public EmployeeDAO()
{
//
// TODO: Add constructor logic here
//
}
public IQueryable BindEmployees(int startRowIndex, int maximumRows)
{
EmployeeInfoDataContext dbEmp = new EmployeeInfoDataContext();
var query = from emp in dbEmp.Employees
join dept in dbEmp.Departments
on emp.DeptID equals dept.DeptID
select new
{
EmpID = emp.EmpID,
EmpName = emp.EmpName,
Age = emp.Age,
Address = emp.Address,
DeptName = dept.DepartmentName
};
return query.Skip(startRowIndex).Take(maximumRows);
}
public int GetEmployeeCount()
{
EmployeeInfoDataContext dbEmp = new EmployeeInfoDataContext();
return (from emp in dbEmp.Employees
select emp).Count();
}
}
In the above code, the LINQ query that fetches the employee record uses join operator to get the department name from the Department table(Refer BindEmployees method). We use Skip and Take operator to fetch the records that belongs to the current page.
The GetEmployeeCount() method will get the number of employees available in the table using LINQ query to construct the page numbers.
Now, set the TypeName of ObjectDataSource control to EmployeeDAO and configure the other required properties. Next, set the GridView control DataSourceID property to the ObjectDataSource ID, enable the AllowPaging to true and set the PageSize property (i have set it as 3).
The final code will look like,
<asp:GridView ID="gvEmployee" DataSourceID="ObjectDataSource1" runat="server" AllowPaging="True"
PageSize="3">
</asp:GridView>
<asp:ObjectDataSource ID="ObjectDataSource1" EnablePaging="true"
runat="server" SelectCountMethod="GetEmployeeCount"
SelectMethod="BindEmployees" TypeName="EmployeeDAO" >
</asp:ObjectDataSource>
Note
The property StartRowIndexParameterName and MaximumRowsParameterName is not required if you use the parameter name as startRowIndex and maximumRows in SelectMethod.
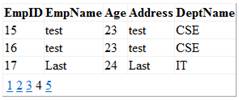
Execute the page and you can see the custom paging in GridView control in action. Refer the below figure,
Download the source Click Here

Comments
Post a Comment